by Martin Goldberg | Apr 20, 2021 | News

Release Date: April 15, 2021
Contact: Christine McMorrow, CALFIRE Information Officer (916) 858-8869
Erin Holland, North Tahoe Fire Information Officer (530) 308-1158
Martin Goldberg, Lake Valley Fire Information Officer (530) 577-3737
Celebrating a Milestone:
Tahoe Program Timberland Environmental Impact Report Certification
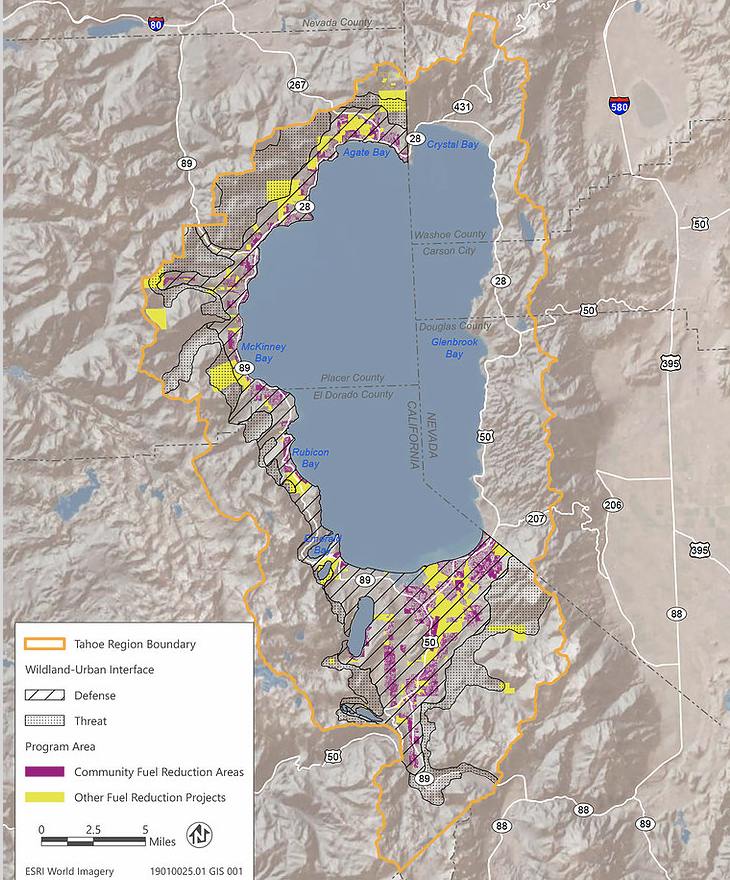
Tahoe City, California April 15, 2021 – On April 07, 2021, the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (CAL FIRE) certified the Tahoe Program Timberland Environmental Impact Report (Tahoe PTEIR or PTEIR) (State Clearinghouse No. 2019069054) and approved the proposed forest management program.
CAL FIRE and the Tahoe Fire and Fuels Team celebrate a milestone with the certification and approval of the Tahoe PTEIR and commend Lake Valley Fire Protection District (LVFPD), California Tahoe Conservancy (CTC), and North Tahoe Fire Protection District (NTFPD) for their proactive efforts to complete the Tahoe PTEIR. Special thanks to Ascent Environmental Inc. and their subcontractors for the invaluable technical support provided throughout this process. The program, which covers approximately 17,480 acres of Wildland Urban Interface on the California side of the Tahoe Basin, supports an increase in the pace and scale of forest management and fuels reduction treatments to approximately 900 – 1,300 acres annually.
The report addresses a long-term program of forest management across private, local jurisdiction, federal, and California Tahoe Conservancy (Conservancy) land. The Tahoe PTEIR includes numerous forest treatment activities including mechanical thinning, manual/hand thinning, prescribed understory burning, pile burning, sale and transport of merchantable timber, and the transport and use of biomass for energy generation and wood pulp products. Herbicide treatment is not proposed.
“This program will advance Tahoe Basin partners’ ability to implement the Multi-Jurisdictional Fuel Reduction and Wildfire Prevention Strategy to reduce the risk of catastrophic wildfires and the potential damage to our forests, watersheds, habitats, and most importantly our communities,” said Steve Leighton, Acting Fire Chief with North Tahoe Fire Protection District. “These treatments will also increase forest resiliency to the effects of climate change we are already experiencing, such as prolonged drought, pest and disease outbreaks and increased tree mortality.”
CAL FIRE prepared the Tahoe PTEIR to evaluate the effects of forest management more efficiently and comprehensively, while improving project approval and delivery processes for fuels reduction activities. Other public agencies may serve as responsible agencies in approving later treatment activities pursuant to State CEQA Guidelines Section 15168 and following California Forest Practice Rules. These responsible agencies, or project proponents, could include CAL FIRE, Conservancy, fire districts, or other public agencies or landowners with land ownership/stewardship responsibilities.
“The Program Timberland Environmental Impact Report project has received funding from the Southern Nevada Public Land Management Act (SNPLMA), which has improved the quality of life for residents and visitors across Nevada and portions of both Arizona and California,” said Robert Wandel, Assistant District Manager, SNPLMA. “We are proud that SNPLMA has added to the protection and improvement of the unique and valuable resources of the Lake Tahoe Basin.”
Brad Zlendick, Fire Chief with Lake Valley Fire Protection District, stated “This showcase of inter-agency collaboration resulted in a true achievement and successful milestone for the Tahoe Basin. The Tahoe PTEIR could not have been accomplished without the forward-thinking vision of key funding partners who were willing to support this project.” The Tahoe PTEIR project development was funded primarily by federally approved SNPLMA funding sources, and seeded by state Water Quality, Supply, And Infrastructure Improvement Act of 2014 funds.
“This Programmatic Timberland EIR is both an important and necessary step for fuels reduction and community safety in the Tahoe Basin. The PTEIR provides a positive step forward in addressing the effects of climate change in this critical area,” stated Chief Thom Porter, CAL FIRE Director and California’s State Forester. “Providing this level of regulatory efficiency helps land managers get projects on the ground quicker to create healthy forest conditions that benefit all Californians. Healthy forests help clean our water and air, they sequester more carbon and are more resilient to pests, disease and catastrophic wildfire.”
The Draft and Final PTEIR are available at https://www.ntfire.net/tahoe-pteir. To prevent the spread of COVID-19, printed copies of the PTEIR will not be available for review at public buildings. Individuals that are unable to access the PTEIR online should contact North Tahoe Fire Protection District at TahoePTEIR@ntfire.net or 530-584-2344.
CAL FIRE served as the lead agency for completion of the PTEIR under CEQA and the California Forest Practices Act. Pursuant to CEQA Guidelines Section 15091, all supporting documents for the PTEIR (i.e., record of proceedings) are available for review during normal business hours at 1416 9th Street, Room 1506-14, Sacramento, CA 95814. The custodian of these documents is Bill Solinsky of CAL FIRE.
by Martin Goldberg | Apr 5, 2021 | News
April 5, 2021
Lake Tahoe prescribed fire operations continue
Contact: USDA Forest Service, Lisa Herron 530-721-3898
LAKE TAHOE, Calif./Nev., April 5, 2021 – Weather and conditions permitting, the Tahoe Fire & Fuels Team will continue prescribed fire operations this week at Lake Tahoe. Smoke may be visible. A map with project locations and detailed information is available for viewing at tahoelivingwithfire.com. Sign-up to receive email prescribed fire notifications by sending a request to pa_ltbmu@fs.fed.us.
Prescribed fires are a vital tool for restoring forest health to fire-adapted ecosystems. Fire is a natural and essential process in the Sierra Nevada that cannot be duplicated by thinning operations alone. Prescribed fires mimic natural, low intensity fires which burn mainly on the forest floor, consuming excess vegetation (fuels), such as small trees and shrubs, allowing mature trees to remain intact. These fires not only reduce ground fuels, they help trees increase resistance to insects and disease leading to a healthier, more resilient forest over time.
Prescribed fire managers use different methods to reintroduce low intensity fire back into our forests that include pile burning and understory burning. Pile burning is intended to remove excess fuels (branches, limbs and stumps) that can feed unwanted wildfires and involves burning slash piles that are constructed by hand and mechanical equipment. Understory burning is low intensity prescribed fire that takes place on the ground (the understory) rather than pile burning. Understory burning uses a controlled application of fire to remove excess vegetation under specific environmental conditions that allow fire to be confined to a predetermined area. Understory burning produces fire behavior and fire characteristics required to attain planned fire and resource management objectives.
Each operation follows a specialized prescribed fire burn plan, which considers temperature, humidity, wind, moisture of the vegetation, and conditions for the dispersal of smoke. All this information is used to decide when and where to burn.
Smoke from prescribed fire operations is normal and may continue for several days after an ignition depending on the project size and environmental conditions. Prescribed fire smoke is generally less intense and of much shorter duration than smoke produced by wildland fires.
Agencies coordinate closely with local, county and state air pollution control districts and monitor weather conditions carefully prior to prescribed fire ignitions. They wait for favorable conditions that will carry smoke up and disperse it away from sensitive areas. Crews also conduct test burns before igniting a larger area, to verify how effectively materials are consumed and how smoke will travel.
Before prescribed fire operations are conducted, agencies post road signs around areas affected by prescribed fire, send email notifications and update the local fire information line maintained by the USDA Forest Service at 530-543-2816. The TFFT gives as much advance notice as possible before burning, but some operations may be conducted on short notice due to the small window of opportunity to conduct these operations.
To learn more about the benefits of prescribed fire, visit https://tahoe.livingwithfire.info/get-informed/understanding-fire/.
###
About the Tahoe Fire and Fuels Team
The Tahoe Fire and Fuels Team (TFFT) consists of representatives of Tahoe Basin fire agencies, CAL FIRE, Nevada Division of Forestry and related state agencies, University of California and Nevada Cooperative Extensions, the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency, the USDA Forest Service, conservation districts from both states, the California Tahoe Conservancy and the Lahontan Regional Water Quality Control Board. Our Mission is to protect lives, property and the environment within the Lake Tahoe Basin from wildfire by implementing prioritized fuels reduction projects and engaging the public in becoming a Fire Adapted Community.
For more information, visit https://tahoe.livingwithfire.info/about/.
by Martin Goldberg | Nov 10, 2020 | News

SOUTH LAKE TAHOE, Calif. – A burn ban in the Lake Tahoe Basin was put in place this summer in response to the unprecedented and extreme fire conditions in California. While there were no major fires in the Basin there were record setting acres burned across the state.
A ban of charcoal barbeques, wood fire pits and open burning was but in place along with extra bans during Red Flag Warning conditions.
With the arrival of winter snow, South Lake Tahoe Fire Rescue and Lake Valley Fire Protection District have lifted the ban in the City of South Lake Tahoe and lake portion of El Dorado County. The Forest Service have not released their ban as of Tuesday morning.
● City of South Lake Tahoe – Charcoal BBQs and cooking fires are allowed. Natural Gas (NG) or Propane (LPG) outdoor firepits and barbecues, and pellet grills/smokers are allowed. Solid fuel recreational/warming fires and open burns are NOT allowed.
● Meyers and El Dorado County portions of the Lake Tahoe Basin – Charcoal BBQs and cooking fires are allowed. Natural Gas (NG) or Propane (LPG) outdoor firepits and barbecues, and pellet grills/smokers are allowed. Solid fuel recreational/warming fires are allowed in properly constructed or manufactured firepits. Open burning is still suspended until further notice.
Local South Lake Tahoe fire agency personnel are telling the public they appreciate their adherence to the recent fire restrictions, but ask they remain cognizant and report hazardous fires by dialing 9-1-1.
It is very important to follow manufacturer recommended instructions on the proper care and maintenance of barbecues and/or firepits.
For more information, contact South Lake Tahoe Fire Rescue at (530) 542-6160 or Lake Valley Fire Protection District (530) 577-3737.